Complete Guide: How to Deploy Windows Updates with Microsoft Intune (Step-by-Step)
Managing Windows updates is a fundamental pillar of security and efficiency in any organization. Keeping operating systems up-to-date protects against vulnerabilities, ensures compliance with IT policies, and introduces new features that can increase productivity. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore how you can use Microsoft Intune to create a robust and automated Windows update deployment strategy, with step-by-step guides and best practices recommended by Microsoft.
Understanding Update Types: Quality vs. Feature
Updates
Before we dive into the configuration, it’s crucial to understand the two main types of Windows updates:
Quality Updates: These are the monthly updates (released on the second Tuesday of each month, “Patch Tuesday”) that include security fixes, bug fixes, and reliability improvements. They are cumulative, meaning the latest update contains all previous fixes.
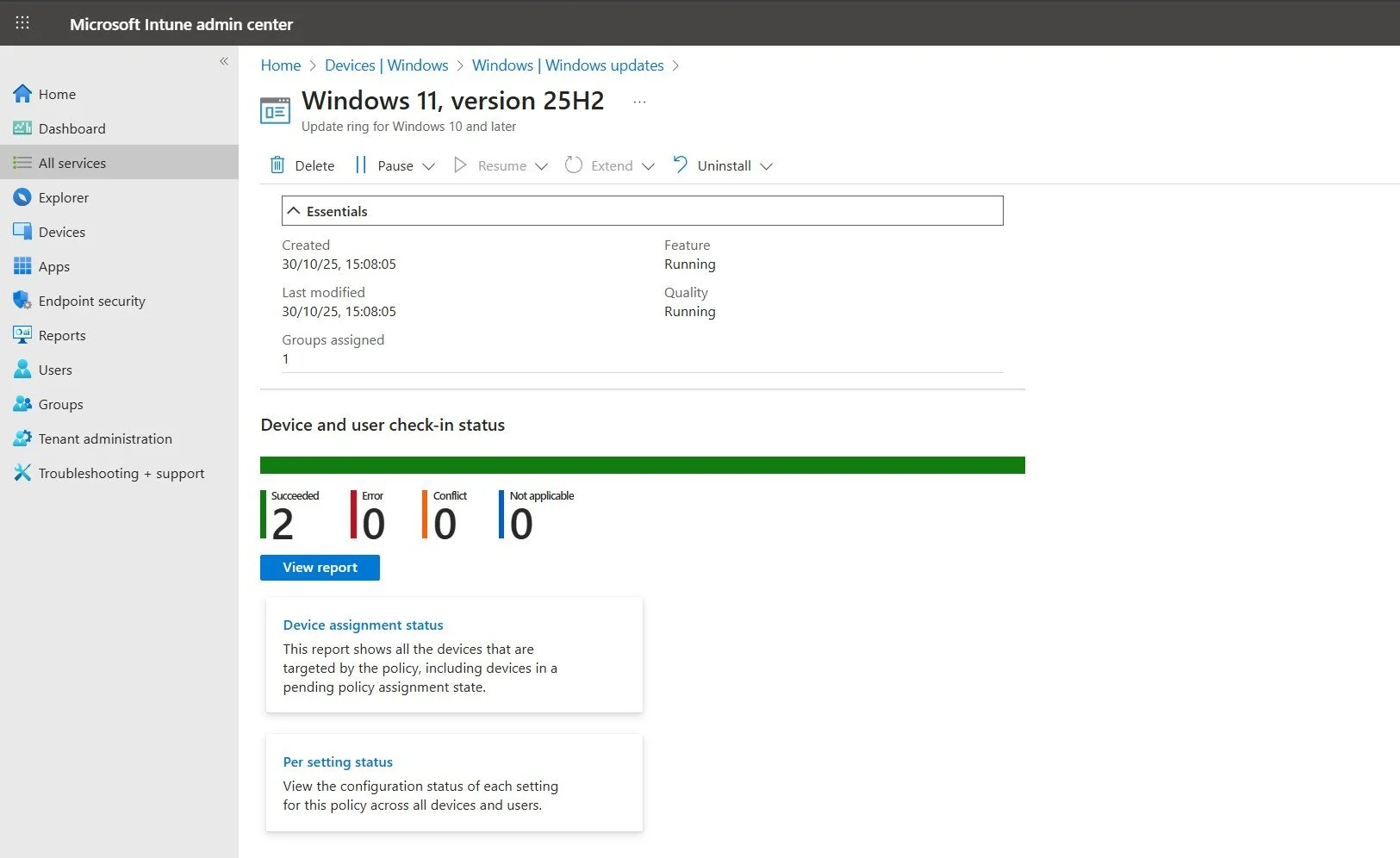
Feature Updates: These are the annual updates that introduce new features and major changes to the operating system (for example, upgrading from Windows 10 to Windows 11, or from Windows 11 22H2 to 23H2). Their implementation requires more planning and testing. Intune offers distinct policies to manage both types effectively.
Step-by-Step Guide 1: Manage Quality Updates with “Update Rings”
Update Rings are the foundation of your monthly patching strategy. They allow for a phased rollout, ensuring that updates are tested before being distributed to the entire organization.
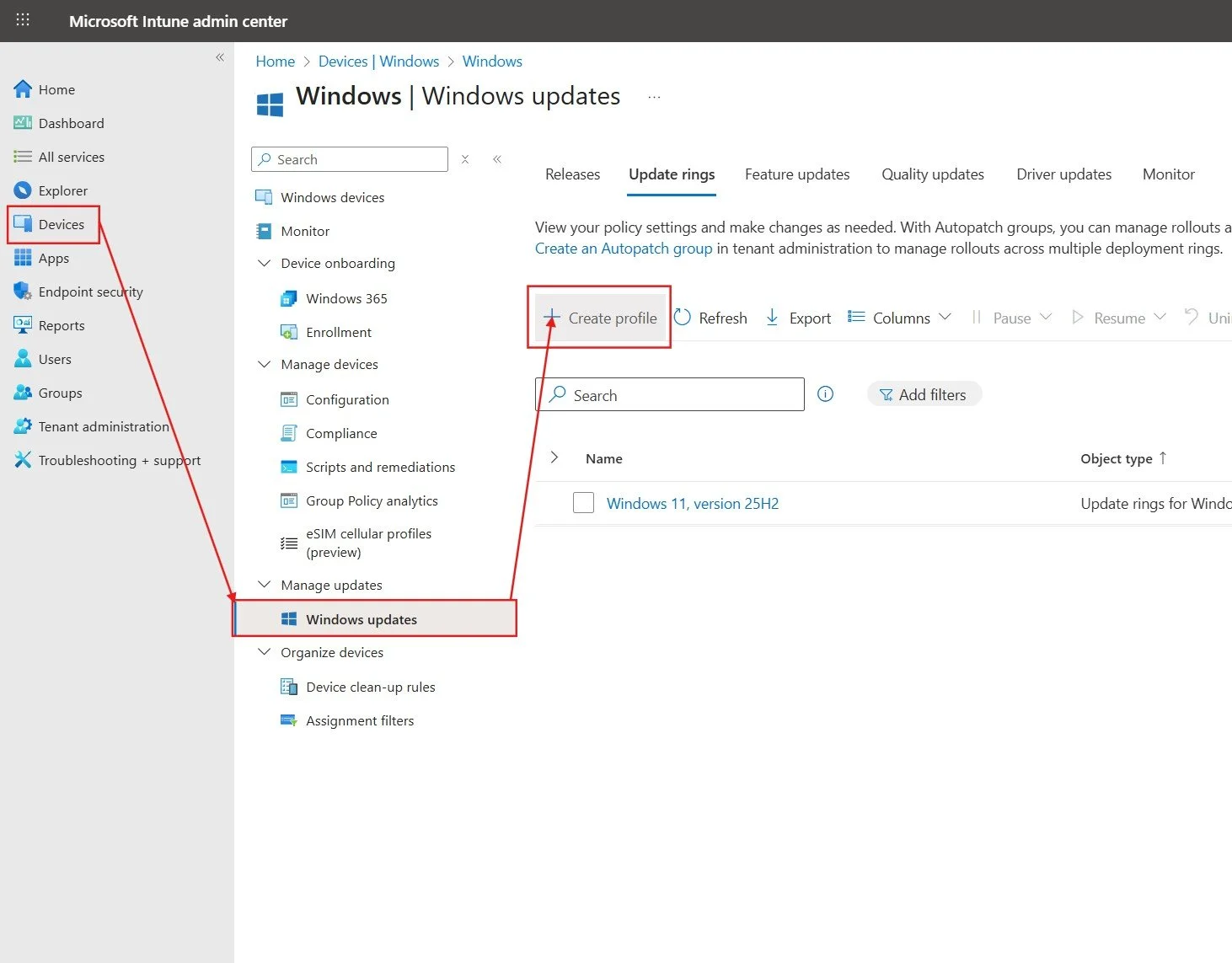
Step 1: Access the Intune Portal and Create a Profile
1. Go to the Microsoft Intune admin center.
2. Navigate to Devices > Windows > Windows 10 and later updates.
3. Select the Update rings tab and click Create profile.
Step 2: Configure the Update Ring Settings
On the creation screen, you will configure the update behavior. For a ring strategy, you will create multiple profiles (e.g., Ring 0 - IT, Ring 1 - Pilot, Ring 2 - Production) with different deferral periods.
Name: Give a descriptive name (e.g., “Windows - Quality Updates - Ring 0 (IT)”).
Microsoft product updates: Select Allow to update other Microsoft applications, such as Office.
Quality update deferral period (days): This is the most important value. It defines how many days the device will wait after the update is released by Microsoft.
Ring 0 (IT): 0 days
Ring 1 (Pilot): 3-5 days
Ring 2 (Production): 7-14 days
Active hours: Set the working hours (e.g., 8:00 AM to 6:00 PM) to prevent automatic reboots during this period.
Automatic update behavior: Select Auto install at maintenance time. This is the most common option to ensure that updates are installed without user intervention.
Step 3: Assign the Profile
Assign the policy to a Microsoft Entra ID (formerly Azure AD) device group that corresponds to your deployment ring. Repeat these steps for each ring, adjusting the deferral period.
Step-by-Step Guide 2: Manage Feature Updates with Dedicated Policies
On the same screen (Devices > Windows > Windows 10 and later updates), select the Feature updates tab.
Click Create profile
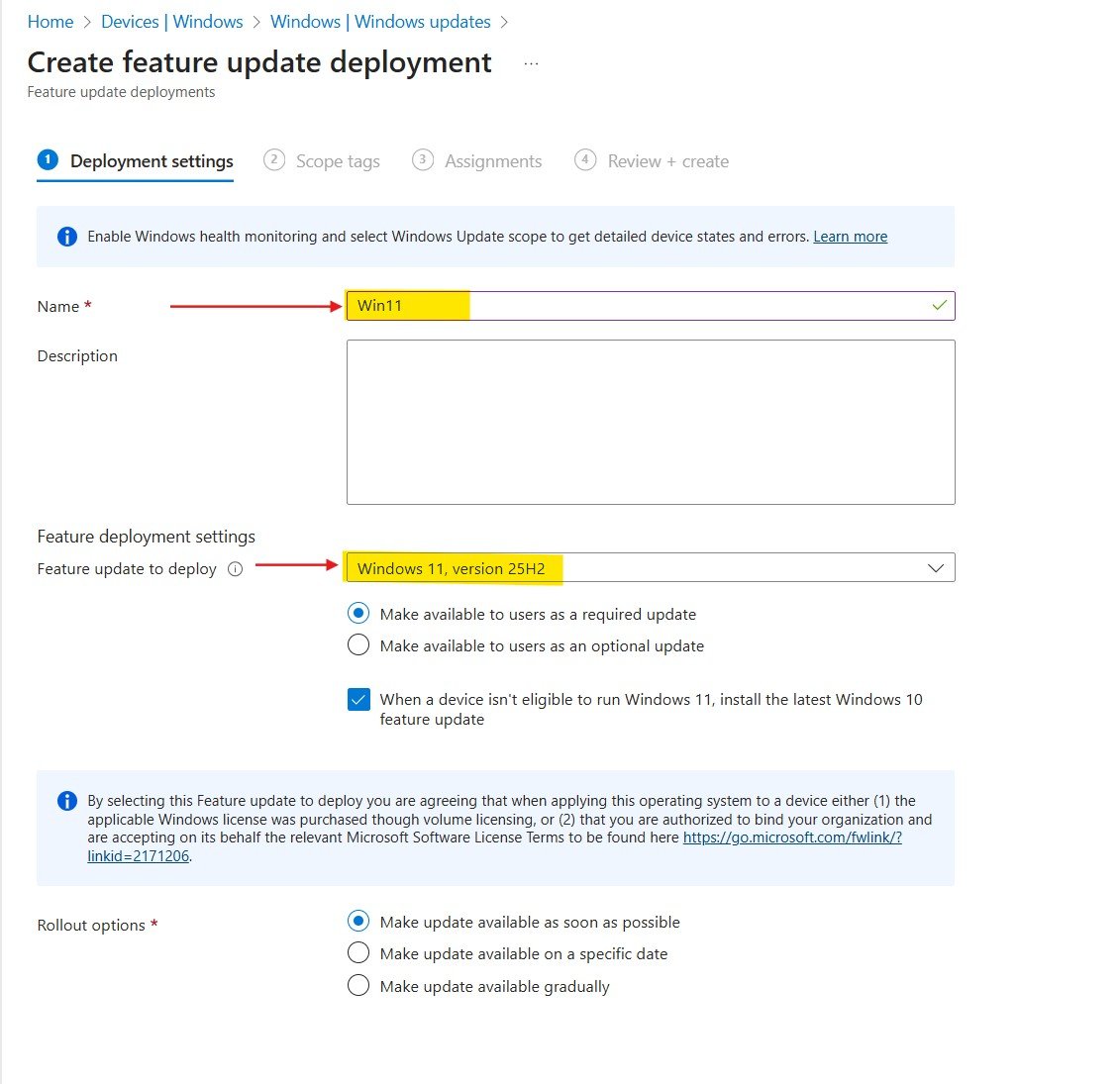
Step 2: Define the Windows Version
Name: Give a descriptive name (e.g., “Windows - Feature Update - Maintain 23H2”).
Feature update to deploy: Select the Windows version you want your devices to run. Devices will not be updated to any version later than this. For example, if you select Windows 11 23H2, eligible devices will be updated to this version and remain on it.
Step-by-Step Guide 3: Expedite Critical Updates with “Expedite Updates”
In the event of a critical security vulnerability (zero-day), you can’t wait for the deferral periods. The Expedite Quality Updates feature allows you to force the installation of a security update as quickly as possible.
Navigate to Devices > Windows > Windows 10 and later updates and select the Quality updates tab.
Click Create profile.
Name: Give a name (e.g., “Expedite - Log4j Patch - Dec 2025”).
Expedite installation of quality updates if device OS version is less than: Select the update you want to force. Intune shows the latest security updates.
Number of days to wait before restart is enforced: Set to 0 or 1 day to force the reboot and ensure protection is applied quickly.
Assign this policy to the “All Devices” group or to specific groups for a quick and effective response to threats.
Conclusion
Implementing a Windows update strategy with Microsoft Intune not only improves security and compliance but also optimizes the management of your devices. By combining Update Rings for monthly patching, Feature Update Policies to control OS versions, and Expedite Updates for emergencies, you can ensure that your systems are always up-to-date with minimal impact on users.
💡 Want to optimize your endpoint management and strengthen your organization’s security? Get in touch to explore how Modern Workplace Management solutions can help your business.