How to Configure Windows Update Rings in Microsoft Intune: A Step-by-Step Guide
Short Summary: A complete, step-by-step guide for IT administrators on how to implement a robust, phased deployment strategy for Windows updates using Deployment Rings in Microsoft Intune. Learn to build a three-ring model to test, validate, and deploy updates with confidence, minimizing risk and ensuring fleet stability.
The Challenge of Managing Windows Updates
In any organization, managing Windows updates is a critical but challenging task. The constant flow of quality and feature updates is essential for security and productivity, but an uncontrolled rollout can lead to business disruptions, application compatibility issues, and a poor user experience. Pushing updates to all devices simultaneously is a high-risk strategy that can turn a minor issue into a widespread crisis.
This is where a structured, phased deployment strategy becomes essential. By using Deployment Rings in Microsoft Intune, IT administrators can transform update management from a reactive, stressful process into a proactive, controlled, and automated workflow. This approach allows you to test updates on a small group of pilot users, validate them with a broader set of early adopters, and then confidently deploy them to the entire organization, minimizing risk and ensuring stability.
This guide provides a complete, step-by-step methodology for implementing a robust Windows Update ring strategy using Microsoft Intune. We will build a three-ring model that aligns with industry best practices, ensuring your device fleet remains secure, compliant, and up-to-date with minimal administrative overhead.
What are Deployment Rings?
Deployment Rings are a core concept of Windows as a Service, designed to manage the rollout of updates in controlled phases. Instead of deploying an update to all devices at once, you create a series of groups (rings) that receive the update sequentially. This allows you to test for any potential issues on a small, low-impact group before the update reaches business-critical systems.
A typical and highly effective strategy involves three rings:
- Ring 1: IT & Pilot Users (The "Canaries"). This first ring consists of IT administrators and a small group of tech-savvy pilot users. They receive updates immediately upon release (0-day deferral). Their role is to catch any immediate technical issues, driver conflicts, or problems with core IT services.
- Ring 2: Early Adopters (The "Business Validators"). This ring is a representative sample of users from various business departments. They receive the update after it has been validated by Ring 1 (e.g., 3 days for quality updates, 7 days for feature updates). This phase is crucial for testing compatibility with line-of-business (LOB) applications and ensuring the update doesn't disrupt daily workflows.
- Ring 3: Broad Deployment (The "Production Users"). This final ring includes all remaining users in the organization. They receive the update only after it has been successfully validated by both Ring 1 and Ring 2 (e.g., 7 days for quality updates, 14 days for feature updates), ensuring a stable and seamless experience for the majority of the workforce.
This phased approach provides a safety net, allowing you to pause or roll back the deployment if any issues are discovered, thereby protecting the organization from widespread disruption.
Prerequisites
Before configuring your update rings, ensure your environment meets the following requirements.
| Requirement | Details |
|---|---|
| Intune Subscription | An active Microsoft Intune Plan 1 or higher subscription. |
| Supported Windows Editions | Windows 10/11 Pro, Enterprise, Education, or Business. |
| Device Enrollment | Devices must be enrolled in Microsoft Intune and be Microsoft Entra joined or Hybrid Entra joined. |
| Network Access | Devices must have access to Windows Update endpoints on the internet. |
| Permissions | Your account needs the Policy and Profile Manager built-in role in Intune. |
Step-by-Step Guide: Creating Your Deployment Rings
Our strategy will be based on creating three distinct update rings. The first step is to create the corresponding security groups in Microsoft Entra ID.
Step 1: Create Security Groups for Each Ring
First, we need to create three Microsoft Entra ID security groups to target our policies. You can populate these groups manually or use dynamic membership rules.
- Navigate to the Microsoft Intune admin center.
- Go to Groups > All groups > New group.
- Create the following three groups:
| Group Name | Membership Type | Members |
|---|---|---|
WIN-UR-Ring1-IT-Pilot |
Assigned | Add IT administrators and select pilot users. |
WIN-UR-Ring2-Early-Adopters |
Assigned | Add a representative sample of business users. |
WIN-UR-Ring3-Broad-Deployment |
Assigned or Dynamic | Add all remaining users or devices. A dynamic group with the rule (device.deviceOSType -eq "Windows") can target all Windows devices. |
Pro Tip: For consistency and automation, it is a best practice to assign update rings to device groups rather than user groups. This ensures devices receive their policies regardless of who is signed in.
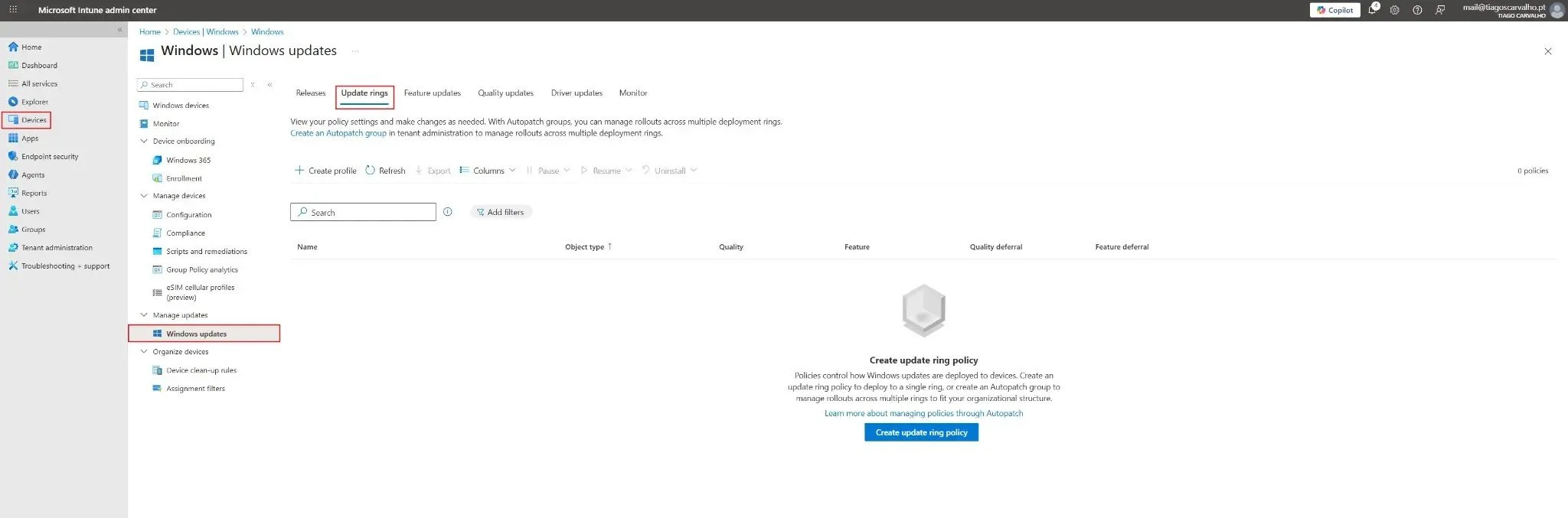
Figure 1: Navigating to the Windows Update Rings section in the Intune admin center (Devices > Windows > Windows updates > Update rings tab).
Step 2: Create Ring 1 - The IT Pilot Ring
This ring is for your IT team and will have no deferrals, ensuring you get updates as soon as they are released by Microsoft.
- In the Intune admin center, navigate to Devices > Windows > Windows 10 and later updates > Update rings tab.
- Click Create profile.
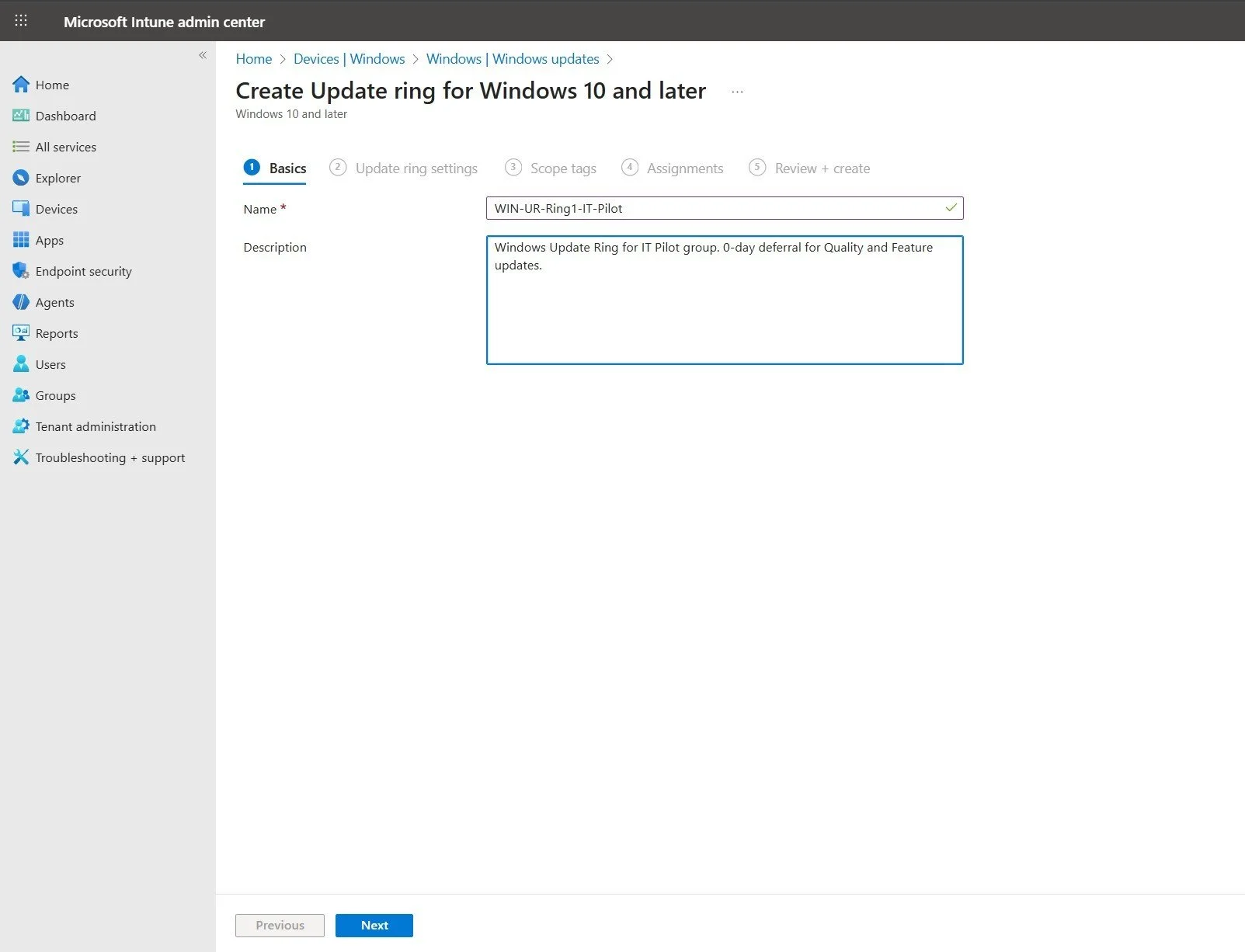
- On the Basics page, enter the following:
- Name:
WIN-UR-Ring1-IT-Pilot - Description:
Windows Update Ring for IT Pilot group. 0-day deferral for Quality and Feature updates.
- Name:
- Click Next.
Figure 2: Creating the profile for the IT Pilot ring with name and description.
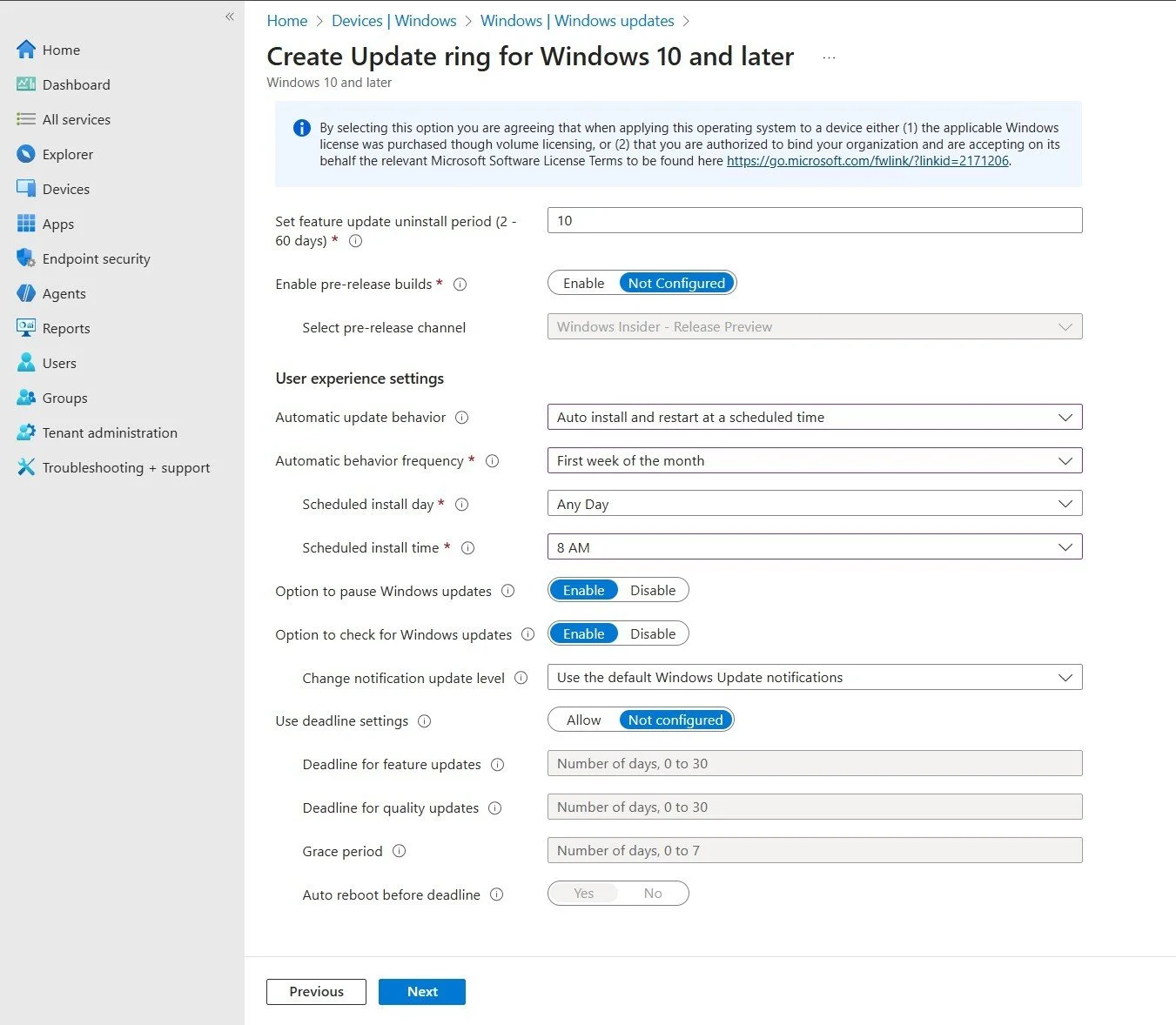
- On the Update ring settings page, configure the following:
- Microsoft product updates: Allow
- Windows drivers: Allow
- Quality update deferral period (days): 0
- Feature update deferral period (days): 0
- Set feature update uninstall period (2-60 days): 10
- Enable pre-release builds: Not Configured
- Upgrade Windows 10 devices to Latest Windows 11 release: Yes (if you are ready to upgrade)
- Automatic update behavior: Auto install and restart at a scheduled time
- Automatic behavior frequency: First week of the month
- Scheduled install day: Any Day
- Scheduled install time: 8 AM
- Option to pause Windows updates: Enable
- Option to check for Windows updates: Enable
- Change notification update level: Use the default Windows Update notifications
- Use deadline settings: Not configured
- Click Next.
Figure 3: Configuring the update and user experience settings for the IT Pilot ring (Ring 1) with 0-day deferrals.
- On the Assignments page, click Add groups, select the
WIN-UR-Ring1-IT-Pilotgroup, and then click Next. - On the Review + create page, verify your settings and click Create.
Step 3: Create Ring 2 - The Early Adopters Ring
This ring is for your business validators and will have a short deferral period to allow for testing after the IT pilot.
- Follow the same steps as above, but use the following settings:
- Basics:
- Name:
WIN-UR-Ring2-Early-Adopters - Description:
Windows Update Ring for Early Adopters. 3-day deferral for Quality, 7-day for Feature.
- Name:
- Update ring settings:
- Quality update deferral period (days): 3
- Feature update deferral period (days): 7
- Set feature update uninstall period: 10 days
- Automatic behavior frequency: First week of the month
- Scheduled install time: 8 AM
- Keep other settings consistent with Ring 1
- Assignments: Assign to the
WIN-UR-Ring2-Early-Adoptersgroup. - Review and Create the profile.
Step 4: Create Ring 3 - The Broad Deployment Ring
This is your production ring for all remaining users. It has the longest deferral period, ensuring updates are thoroughly vetted before a wide rollout.
- Follow the same steps again, using these settings:
- Basics:
- Name:
WIN-UR-Ring3-Broad-Deployment - Description:
Windows Update Ring for Broad Deployment. 7-day deferral for Quality, 14-day for Feature.
- Name:
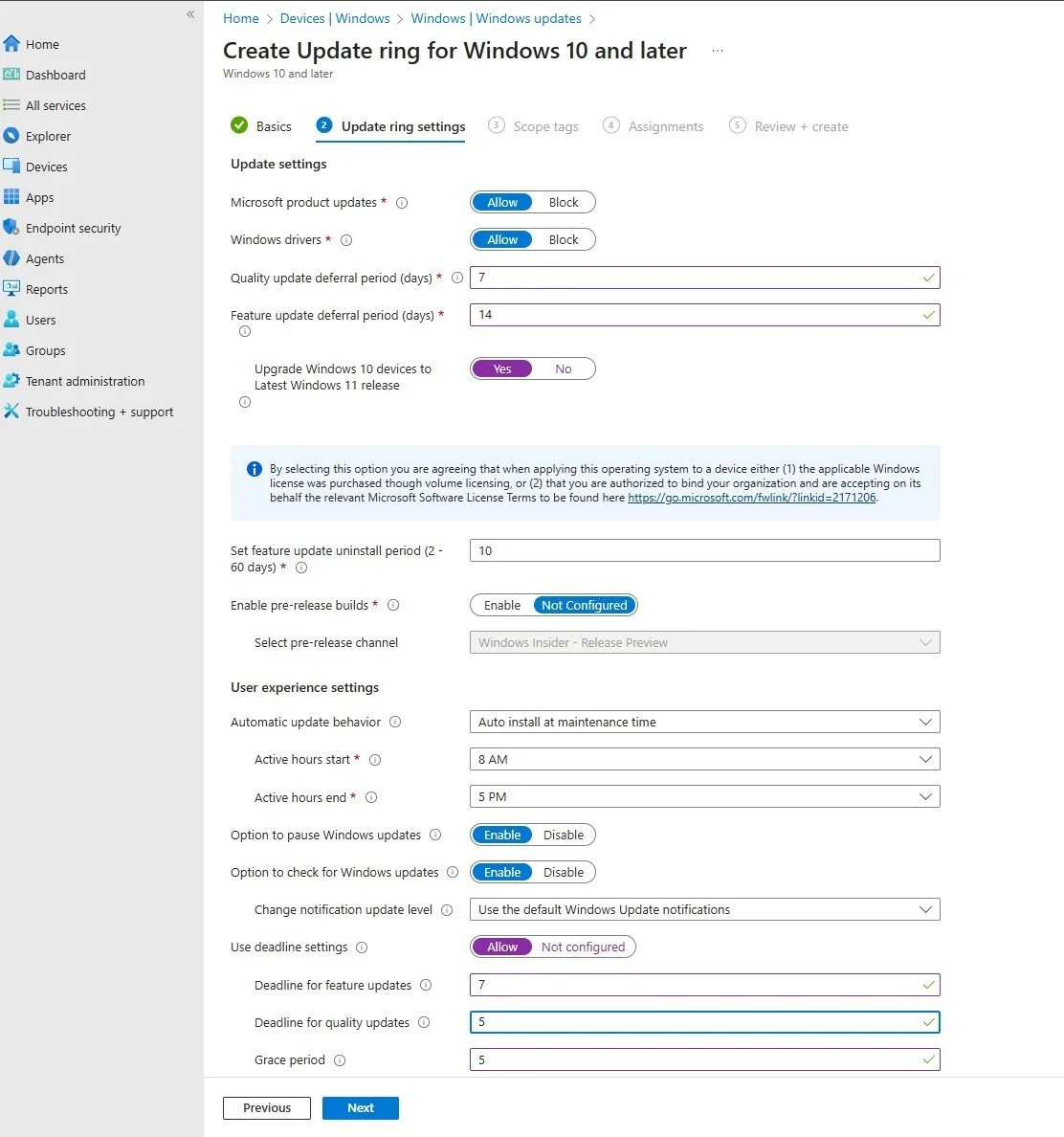
- Update ring settings:
- Quality update deferral period (days): 7
- Feature update deferral period (days): 14
- Set feature update uninstall period: 10 days
- Automatic update behavior: Auto install at maintenance time
- Active hours start: 8 AM
- Active hours end: 5 PM
- Use deadline settings: Allow (with configured deadlines)
- Deadline for feature updates: 7 days
- Deadline for quality updates: 5 days
- Grace period: 5 days
- Assignments: Assign to the
WIN-UR-Ring3-Broad-Deploymentgroup. - Review and Create the profile.
Figure 4: Configuring the settings for the Broad Deployment ring
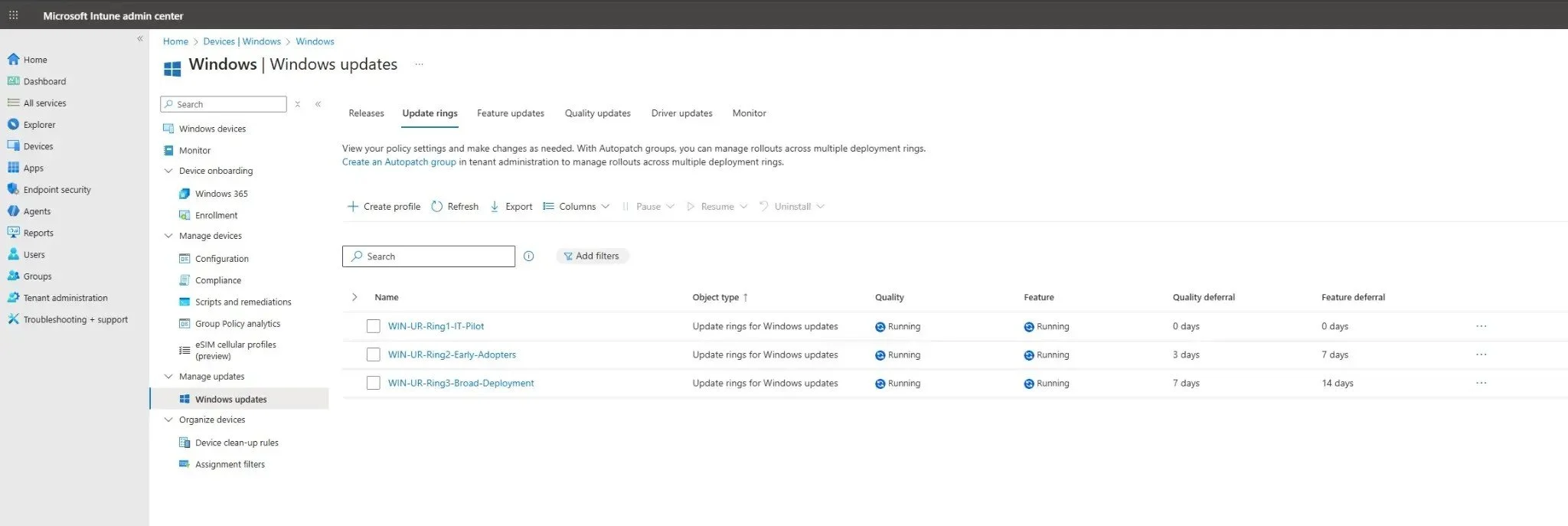
Figure 5: The complete three-ring model is now visible in the Update Rings dashboard, showing all configured policies with their respective deferral periods.
Summary of Recommended Ring Settings
This table provides a clear overview of the recommended configuration for your three-ring model based on the implementation shown in the screenshots.
| Setting | Ring 1: IT Pilot | Ring 2: Early Adopters | Ring 3: Broad Deployment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Target Group | WIN-UR-Ring1-IT-Pilot |
WIN-UR-Ring2-Early-Adopters |
WIN-UR-Ring3-Broad-Deployment |
| Quality Update Deferral | 0 days | 3 days | 7 days |
| Feature Update Deferral | 0 days | 7 days | 14 days |
| Feature Update Uninstall Period | 10 days | 10 days | 10 days |
| Automatic Behavior | Auto install and restart at scheduled time | Auto install and restart at scheduled time | Auto install at maintenance time |
| Scheduled Install Time | 8 AM | 8 AM | N/A (maintenance time) |
| Active Hours | N/A | N/A | 8 AM - 5 PM |
| Deadline Settings | Not configured | Not configured | Quality: 5 days Feature: 7 days Grace: 5 days |
Best Practices for Managing Update Rings
Monitor Compliance: Regularly check the Device and user check-in status report for each ring to monitor for errors and ensure devices are updating successfully. Navigate to Reports > Windows updates > Windows Update for Business reports to access detailed compliance data.
Use the Pause Button: If Ring 1 or Ring 2 users report a critical issue with an update, you can Pause the affected ring to prevent the update from deploying further. You can pause updates for up to 35 days, giving you time to investigate and resolve the issue.
Manage Driver Updates: While enabling driver updates is convenient, it can sometimes introduce instability. Monitor your pilot rings closely. If you encounter issues, you can set Windows drivers to Block and manage drivers through a more controlled process using driver update policies.
Communicate with Users: Inform users, especially those in the pilot rings, about the strategy. Create a Teams channel or email distribution list where they can report issues and provide feedback. This creates a feedback loop that improves the overall update process.
Test LOB Applications: Ensure that Ring 2 includes users who rely on critical line-of-business (LOB) applications. Their feedback is essential for catching application compatibility issues before the update reaches the broader organization.
Understanding Deadline Settings
Deadline settings are a powerful feature in Ring 3 that enforce update installation after a specified period. In the configuration shown, Ring 3 uses the following deadlines:
- Quality Update Deadline: 5 days after the update becomes available to the device
- Feature Update Deadline: 7 days after the update becomes available to the device
- Grace Period: 5 days, giving users additional time before a forced restart
This ensures that even if users postpone updates, they will eventually be installed automatically, keeping the fleet compliant and secure. For Ring 1 and Ring 2, deadlines are not configured, allowing IT and early adopters more flexibility to manage their own update schedules.
Conclusion
By implementing a three-ring model for Windows updates in Microsoft Intune, you transform a high-risk, manual process into a controlled, automated, and secure workflow. This strategy not only protects your organization from update-related disruptions but also ensures your devices are consistently patched against the latest security threats. It embodies the principles of proactive IT management—Audit, Harden, and Automate—allowing you to maintain a healthy and secure device fleet with confidence.
The phased approach demonstrated in this guide provides a safety net that catches issues early, validates updates with real users, and only then deploys to the entire organization. This is the foundation of a modern, resilient Windows update strategy that scales with your organization's needs.
References
- Configure Windows Update rings policy in Intune - Microsoft Learn
- Manage Windows software updates in Intune - Microsoft Learn
Author: Tiago S. Carvalho | Website: www.tiagoscarvalho.com